Investigating the inattentive brain...
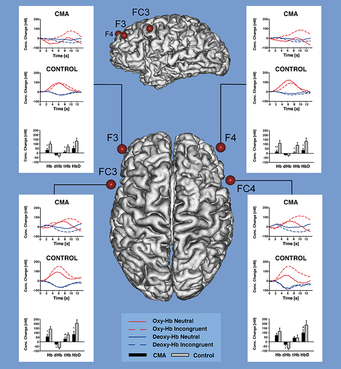
Optical imaging (NIRS) is a method that is particularly suited to investigations of cognitive development and its diseases. Accordingly, we applied the method to children suffering from attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). We were able to demonstrate that functions of the prefrontal cortex are altered during a Stroop task. Subsequent studies aim to identify treatment effects. Another part of this project investigates cerebral microangiopathy that finally leads to vascular dementia. We were able to demonstrate that alterations in frontal cortices are closely related to attentive and executive deficits. Besides optical imaging, we are applying MRI and SPECT.
Related references:
R. Scheid, S. Frisch, M. L. Schroeter
Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system - Treatment with steroids? Journal of Clinical Pharmacy & Therapeutics (2009) 34: published online. IF 1.4
M. L. Schroeter, S. Cutini, M. W. Wahl, R. Scheid, D. Y. von Cramon
Neurovascular coupling is impaired in cerebral microangiopathy – An event-related Stroop study. NeuroImage 34(2007): 26-34. IF 6.2
R. Scheid, C. Preul, T. Lincke, G. Matthes, M. L. Schroeter, T. Guthke, D. Y. von Cramon, O. Sabri
Correlation of cognitive status, MRI- and SPECT-imaging in CADASIL patients. European Journal of Neurology 13(2006): 363-370. IF 2.0
S. J. Moser, S. Cutini, P. Weber, M. L. Schroeter
Right prefrontal brain activation due to Stroop interference is altered in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder - An fNIRS study. Psychiatry Research - Neuroimaging (2009): In press. IF 2.8