Investigating the oscillating brain
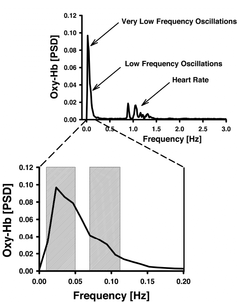
This project investigates changes of spontaneous hemodynamic oscillations during healthy aging and dementia. Recently, using optical imaging (NIRS), we were able to show that spontaneous oscillations specifically around 0.1 Hz decrease in the visual cortex of the aging brain and in vascular dementia (cerebral microangiopathy). Interestingly, this kind of analysis in the frequency domain was much more sensitive in detecting changes than functional visual stimulation. Hence, we aim to establish our approach as a screening method to investigate vascular reagibility. In the future, we want to extend these approaches to optical topography, covering the whole outer brain & fMRI. Moreover, we will examine patients with Parkinson’s & Alzheimer’s Disease and explore the predictive potential of this method to address changes from mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to Alzheimer’s disease. Finally, we want to examine alterations in transgenic mouse models of healthy aging and Alzheimer’s disease.
Related references:
O. Schmiedel, T. J. Nurmikko, M. L. Schroeter, R. Whitaker, J. N. Harvey
Alpha adrenoceptor agonist induced microcirculatory oscillations are reduced in diabetic neuropathy. Microvascular Research 76(2008): 124-131. IF 2.5
K. Müller, J. Neumann, M. Grigutsch, D. Y. von Cramon, G. Lohmann
Detecting groups of coherent voxels in fMRI data using spectral analysis and replicator dynamics. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 26(2007): 1642-1650. IF 2.6
O. Schmiedel, M. L. Schroeter, J. N. Harvey
Microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes indicates impaired microvascular vasomotion and perfusion. American Journal of Physiology: Heart and Circulatory Physiology 293(2007): H3424-H3431. IF 3.7
M. L. Schroeter, M. M. Bücheler, C. Preul, R. Scheid, T. Guthke, O. Schmiedel, D. Y. von Cramon
Corrigendum to Spontaneous slow hemodynamic oscillations are impaired in cerebral microangiopathy. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 27(2007): 1094.
K. Müller, J. Neumann, G. Lohmann, T. Mildner, D. Y. von Cramon
The correlation between BOLD signal strength and latency. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 21(2005): 489-494. IF 2.5
M. L. Schroeter, M. M. Bücheler, C. Preul, R. Scheid, T. Guthke, O. Schmiedel, D. Y. von Cramon
Spontaneous slow hemodynamic oscillations are impaired in cerebral microangiopathy. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 25(2005): 1675-1684. IF 5.7
K. Müller, G. Lohmann, J. Neumann, M. Grigutsch, T. Mildner, D. Y. von Cramon
Investigating the wavelet coherence phase of the BOLD signal. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 20(2004): 145-152. IF 2.9
M. L. Schroeter, O. Schmiedel, D. Y. von Cramon
Spontaneous low frequency oscillations decline in the aging brain. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 24(2004): 1183-1191. IF 5.7
K. Müller, T. Mildner, G. Lohmann, D. Y. von Cramon
Investigating the stimulus-dependent temporal dynamics of the BOLD signal using spectral methods. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 17(2003): 375-382. IF 2.7
K. Müller, G. Lohmann, V. Bosch, D. Y. von Cramon
On multivariate spectral analysis of fMRI time series. NeuroImage 14(2001): 347-356. IF 7.9
